8
9
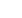
After the alveolar ridge incision and the flap
formation, the three molars were extracted
and the wisdom tooth 18 was extracted using
osteotomy
(Fig. 34)
. Sufficient autologous bone
chips were harvested in the process,which were then
ground in the bone mill and mixed with xenogenous
bone substitute material (Bio-Oss
®
, Geistlich) [7]
to augment the bone defects identified virtually
beforehand. We covered the augmentation ma-
terial with a resorbable collagen membrane (Bio-
Gide
®
, Geistlich) and closed the soft tissue with
individual button sutures
(Fig. 35 to 37)
.
Insertion of the immediate
temporary restoration
To prevent the polymer entering the screw channels
of the titanium caps, we covered these prior to
polymerization with cotton pellets and then
“adhered” the temporary restoration tension
free
(Fig. 38 and 39)
. The patient left the practice
on the day of the surgical procedure with a screw-
retained, temporary, fixed denture and detailed
instructions on food intake. This means a diet con-
sisting of only soft foods for the first two weeks
and in the subsequent four weeks slowly shifting
to more solid food. During the procedure the
patient was administered 1000 mg amoxicillin as
antibioticprophylaxis.Hewasrepeatedlyandclearly
instructed to abstain from nicotine as much as
possible in the postoperative period.
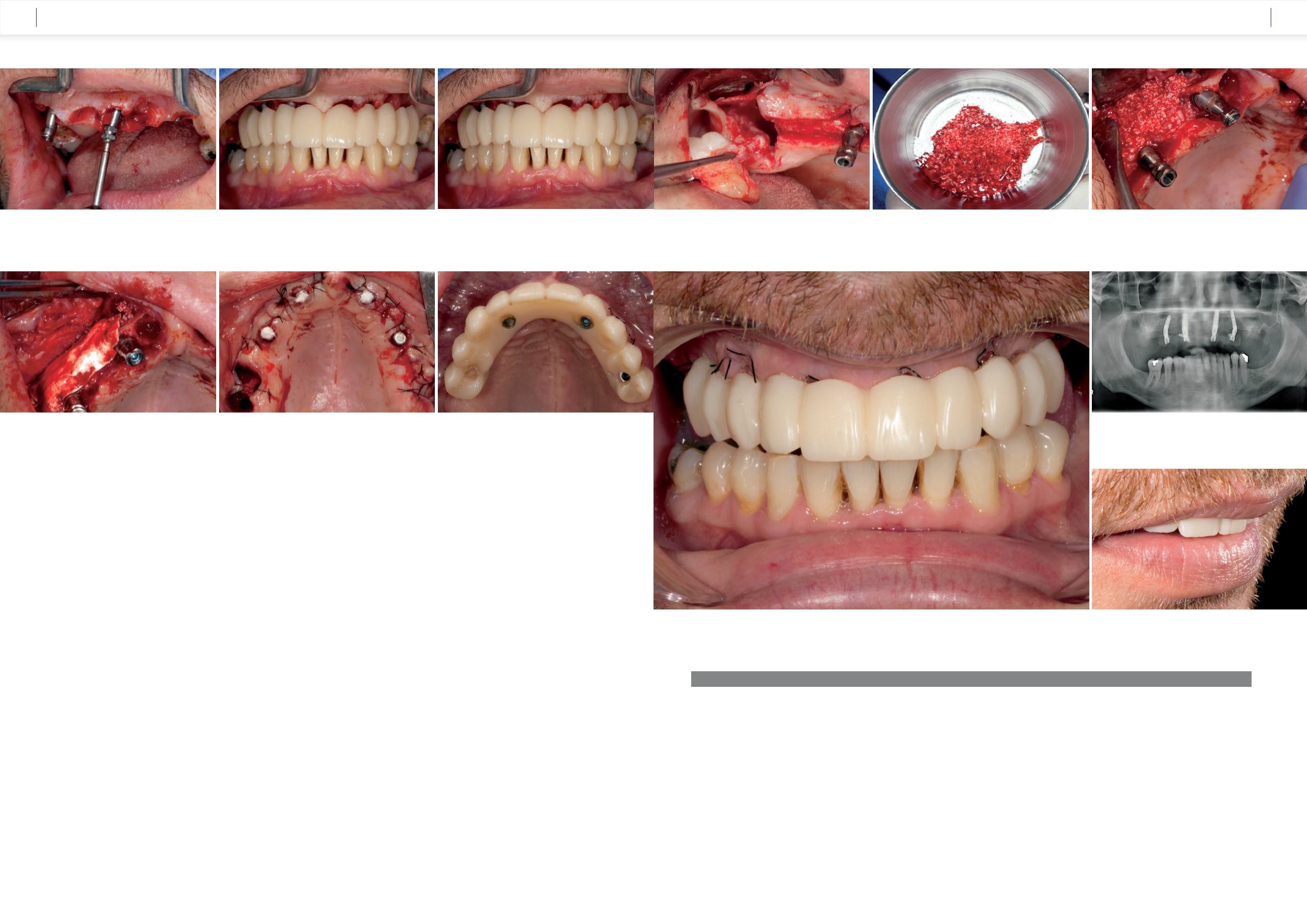
Figure 40
shows soft tissue completely free of
signs of irritation just a few days after surgery.
After two weeks the sutures were removed. A
follow-up radiograph was prepared and the occlu-
sion of the temporary restoration was checked and
minor corrections were made
(Fig. 41 and 42).
Conclusion
The screw-retained, fixed reconstruction on four
implants is a treatment concept that reduces both
effort and costs. Immediate temporary restoration
using the Maló Clinic protocol has been scienti-
fically documented. Pre-implantation planning
taking into account the surgical and prosthetic re-
quirements is given special priority. With the help
of 3D planning in the form of backward planning
[8], implants can be positioned in the software in
the precise angle (0°, 17°, and 30°) relative to
one another, and the screw channels do not have
any negative effects on either the esthetics or the
function.
The new COMFOUR
™
System is highly suitable for
using with this treatment concept [9]. The angled
bar abutments are available in different gingival
heights and as type A or B. The insertion of the
abutments in the correct position is safe and easy
using the attached handle. To screw the abutment
screws in, the flexible handle can be simply
pushed to one side.
The new design of the bar abutments, which omits
the bend, has a positive effect on the soft tissue
augmentation. An additional feature is the align-
ing tools that are helpful for precisely positioning
the cams. The concept is exceptionally well suited
for providing edentulous patients with fixed, im-
mediate temporary restorations in one surgical
procedure.
[1] Maló P, de Araújo Nobre M, Lopes A, Moss SM, Molin GJ.
A longitudinal study of the survival of All-on-4 implants in the
mandible with up to 10 years of follow-up. J Am Dent Assoc
2011;142(3):310−20.
[2] Sheng L, Silvestrin T, Zhan J, Wu L, Zhao Q, Cao Z, Lou Z, Ma
Q, Replacement of severely traumatized teeth with immediate im-
plants and immediate loading: literature review and case reports.
Dent Traumatol. 2015 Jul 14. doi: 10.1111/edt.12201.
[3] Agliardi E, Panigatti S, Clericó M, Villa C, Maló P. Immediate
rehabilitation of the edentulous jaws with full fixed prostheses
supported by four implants: interim results of a single cohort pros-
pective study. Clin. Oral Impl. Res. 21, 2010; 459–465.
[4] Ackermann KL, Kirsch A, Nagel R, Neuendorff G. Mit Backward
Planning zielsicher therapieren. Teil 1: Implantat-prothetische Be-
handlungsbeispiele teamwork J Cont Dent Educ 2008: 466−484.
[5] Kirsch A, Nagel R, Neuendorff G, Fiderschek J, Ackermann KL.
Backward Planning und dreidimensionale Diagnostik,Teil 2: Scha-
blonengeführte Implantation nach CT-basierter 3D-Planung mit
sofortiger Eingliederung des präfabrizierten Zahnersatzes – ein
erweitertes Backward Planning-Konzept. teamwork J Cont Dent
Educ 2008: 734−754.
[6] Maló P, de Araújo Nobre MA, Lopes AV, Rodrigues R.
Immediate loading short implants inserted on low bone
quantity for the rehabilitation of the edentulous maxilla
using an All-on-4 design. J Oral Rehabil. 2015 Aug;42(8):
615-23. doi: 10.1111/joor.12291. Epub 2015 Mar 10.
[7] Pang C1, Ding Y, Zhou H, Qin R, Hou R, Zhang G, Hu K. Al-
veolar ridge preservation with deproteinized bovine bone
graft and collagen membrane and delayed implants. J Cra-
niofac Surg. 2014 Sep;25(5):1698–702. doi: 10.1097/
SCS.0000000000000887.
[8] Venezia P, Lacasella P, Cordaro L, Torsello F, Cavalcanti R. The
BARI technique: a new approach to immediate loading. Int J Est-
het Dent. 2015 Autumn;10(3):428–43.
[9] Randelzhofer P, Cacaci C. Verschraubte Lösung - implantatge-
tragene Restauration im zahnlosen Oberkiefer. teamwork J Cont
Dent Educ 2011: 294−300.
LITERATURE
Fig. 31:
The titanium caps were screwed onto the bar
abutments.
Fig. 32:
To check the esthetics and occlusion, the provisional PMMA
bridge was inserted…
Fig. 33:
… and the tension-free fit around the titanium caps was
checked.
Fig. 37:
The augmentation material was covered
with a resorbable membrane (Bio-Gide
®
, Geistlich).
Fig. 39:
The titanium caps of the COMFOUR
™
system were polymerized
free of tension in the immediate temporary restoration.
Fig. 38:
Using individual button sutures, the soft tissue was closed, and
the screw channels were covered with cotton pellets prior to the cold-cure
polymerization.
Fig. 34:
The remaining teeth were extracted and the osteotomy
of the displaced wisdom tooth was carried out.
Fig. 35:
The bone chips obtained during the osteotomy were ground
and mixed with bone substitute material (Bio-Oss
®
, Geistlich).
Fig. 36:
The virtually identified bone deficits were augmented
with the bone mixture.
Fig. 40:
At the follow-up three days after the surgical procedure, the soft tissue was free of inflammation and well adapted.
Fig. 41:
The follow-up radiograph shows the angulated, well-anchored
implants with the angled COMFOUR™ bar abutments.
Fig. 42:
The occlusal screw-retained temporary restoration forms an
harmonious and esthetic lip line.
CASE STUDY
CASE STUDY